
Bacterial genes in the aphid genome: absence of functional gene transfer from Buchnera to its host. This paper describes HGT between Wolbachia spp., an intracellular bacterial symbiont, and its multicellular eukaryotic insect hosts. Widespread lateral gene transfer from intracellular bacteria to multicellular eukaryotes. Low species barriers in halophilic archaea and the formation of recombinant hybrids. Naor, A., Lapierre, P., Mevarech, M., Papke, R. Genetic transfer in Halobacterium volcanii. A multicopy plasmid of the extremely thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus effects its transfer to recipients by mating. Schleper, C., Holz, I., Janekovic, D., Murphy, J. Cell fusion and hybrids in Archaea: prospects for genome shuffling and accelerated strain development for biotechnology. Gene transfer agents: phage-like elements of genetic exchange. Extracellular DNA metabolism in Haloferax volcanii. Bacterial transformation: distribution, shared mechanisms and divergent control. Johnston, C., Martin, B., Fichant, G., Polard, P. The genome of cultivated sweet potato contains Agrobacterium T-DNAs with expressed genes: an example of a naturally transgenic food crop. Conjugative plasmids: vessels of the communal gene pool. Bacteria–human somatic cell lateral gene transfer is enriched in cancer samples. Expression of multiple horizontally acquired genes is a hallmark of both vertebrate and invertebrate genomes. Darwinian evolution in the light of genomics. Endosymbiotic gene transfer: organelle genomes forge eukaryotic chromosomes. Gene transfer and diversification of microbial eukaryotes. This letter proposes a model for ongoing HGT in eukaryotes involving unicellular and early developmental stages to overcome the barrier of genome sequestration in eukaryotes.Īndersson, J. Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotes: the weak-link model.
Horizontal gene transfer in the acquisition of novel traits by metazoans. This paper examines the impact of expression level on the transferability of a gene in both environmental and laboratory populations of E. High expression hampers horizontal gene transfer. Horizontal gene transfer, genome innovation and evolution. The role of reticulate evolution in creating innovation and complexity. Horizontal transfer, not duplication, drives the expansion of protein families in prokaryotes. Gene recombination in the bacterium Escherichia coli. In view of the use of GM crops and microbes in agricultural settings, in this mini-review we focus particularly on the presence and role of MGE in soil and plant-associated bacteria and the factors affecting gene transfer.Tatum, E. This review summarizes the present state of knowledge on HGT between bacteria as a crucial mechanism contributing to bacterial adaptability and diversity. Thus, for a risk assessment it is important to understand the extent of HGT and genome plasticity of bacteria in the environment.
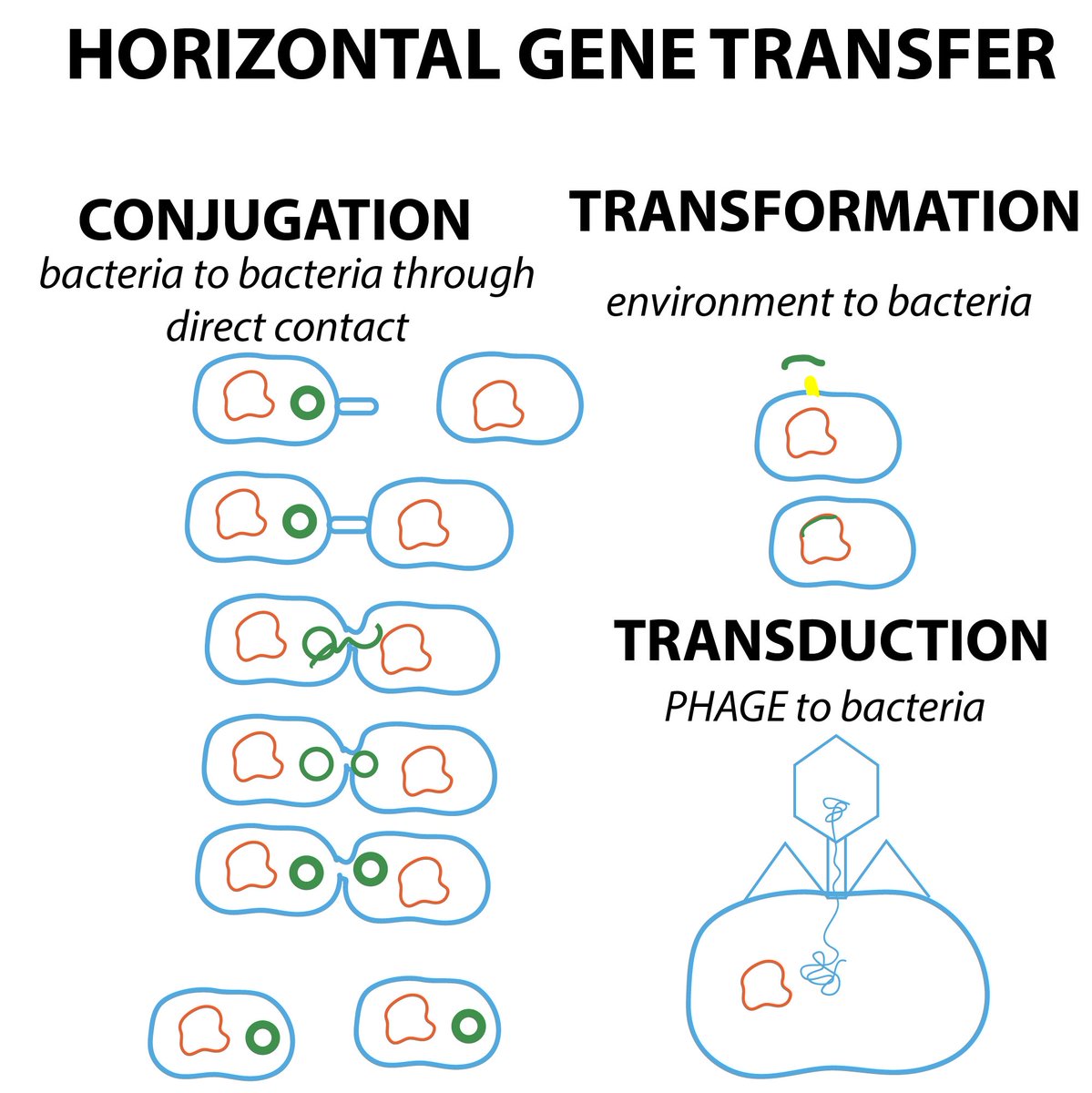
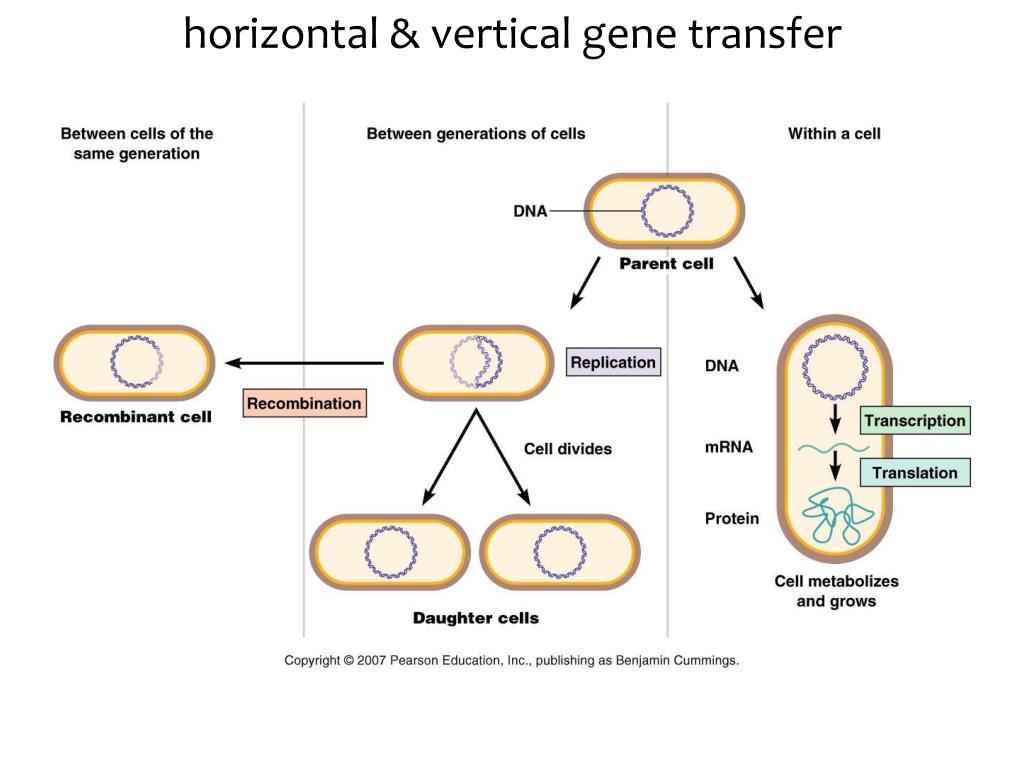
Second, the genetically modified bacterium released into the environment might capture mobile genetic elements (MGE) from indigenous micro-organisms which could extend its ecological potential. First, introduced genetic sequences from a genetically modified bacterium could be transferred to indigenous micro-organisms and alter their genome and subsequently their ecological niche. The occurrence of HGT among bacteria in the environment is assumed to have implications in the risk assessment of genetically modified bacteria which are released into the environment. Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) refers to the acquisition of foreign genes by organisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
